Blood Parasite Infection in Chickens: An Overview
Blood parasite infections, also known as avian malaria, are among the most dangerous diseases affecting chickens, reducing their growth and reproductive performance. These infections are more common during hot and humid months when blood-feeding insects are prevalent and can transmit the disease to chickens.
Although the incidence of blood parasite infections within a flock is relatively low, the damage they cause is significant and comparable to other common infectious diseases in chickens. The mortality rate can be high due to the disease weakening the immune system and causing anemia, which increases the risk of secondary infections.
Blood Parasite Infection in Chickens: An Overview
In Vietnam, the disease frequently occurs in free-range or pasture-raised chickens, with infection rates ranging from 10-50% in breeding chickens, 7-30% in chicks, and 20-50% in adult chickens. Mortality rates are 5-20% in chicks and 10-40% in adults, resulting in substantial economic losses, slow growth rates, and increased culling.
Causes of Blood Parasite Infection
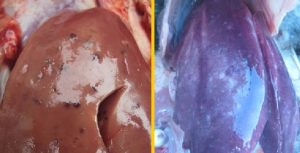
Blood parasite infections in chickens are caused by a protozoan parasite known as Leucocytozoon caulleri, a member of the Haemosporia group within the Protozoa phylum.
When mosquitoes or other blood-feeding insects bite chickens, they transmit the protozoan into the chicken’s bloodstream. The protozoan develops into a parasite within red blood cells, destroying them and spreading to other internal organs, causing a range of dangerous symptoms.
Transmission Pathways
The disease is primarily transmitted through blood-feeding insects like mosquitoes, which spread the protozoan from infected to healthy chickens.
Symptoms of Blood Parasite Infection
Symptoms depend on the specific Leucocytozoon strain and vary with the level of parasitic development and the chicken’s health. The incubation period Thanhga typically ranges from 1 to 2 weeks.
Common symptoms include:
- High fever
- Lethargy and reduced movement
- Loss of appetite
- Pale comb and wattles that turn white over time
- Loss of balance, rapid breathing, and anemia
- Diarrhea with greenish feces; severe cases may include bloody diarrhea
- Oral bleeding in some cases
For laying hens, additional signs include reduced egg production, abnormally small or soft-shelled eggs, and poor hatching rates. Fertility rates and chick survival rates may also decline significantly.
Effective Treatment Protocol
- Immediate Control Measures:
- Clear and clean the entire poultry environment to eliminate hiding places for insects.
- Use insecticides to control mosquitoes and other blood-feeding insects in and around the poultry house.
- Replace bedding with fresh, disinfected material.
- Medication:
- Administer a specialized blood parasite treatment such as VIP-MONO COX according to the manufacturer’s dosage instructions.
- Complement treatment with liver and kidney detoxifiers like HEPASOL-B12.
- Supplement with vitamins A, K3, digestive enzymes, and electrolytes to boost the chickens’ overall health.

Symptoms of Blood Parasite Infection
Preventive Measures
To prevent blood parasite infections:
- Maintain a clean poultry environment and regularly use insecticides to control blood-feeding insects.
- Avoid stagnant water sources where mosquitoes can breed.
- Monitor flock health frequently and enhance overall health with supportive supplements such as vitamins A and K, along with digestive aids.
- Address any disease outbreaks promptly to prevent widespread infections.
>>> Explore more: Bệnh gà
Prevention and Treatment of Blood Parasite Infections in Chickens
Prevention Measures:
- Environmental Hygiene: Regularly clean the environment and use mosquito repellents to prevent mosquito and other blood-feeding insect activity, which is the primary transmission route for the parasites.
- Health Monitoring: Continuously observe the health of your flock, provide appropriate care, and promptly identify and address any signs of illness.
- Supplemental Support: Enhance overall health by supplementing with electrolytes, vitamins, digestive enzymes, and liver and kidney detoxifiers.
Treatment Protocol by Mebipha:
- Reduce Fever: Administer PARA C with a high dosage to quickly lower fever and help chickens recover more rapidly.
- Control Bleeding: Use VITAMIN K WS or VITAMIN K ORAL to prevent bleeding and manage hemorrhagic conditions.
- Parasite Treatment: Apply VIP-MONO COX at a dosage of 1 ml per 10 kg of body weight.
- Liver and Kidney Support: Use AMINO PHOSPHORIC at a dosage of 1 g per 10 kg of body weight or HEPASOL B12 at 1 ml per 10 kg of body weight to detoxify the liver and restore its function. Continue treatment for 3-5 days.

By adhering to these prevention and treatment measures, you can effectively manage and reduce the impact of blood parasite infections in your chickens.
By implementing these strategies, farmers can effectively manage and prevent blood parasite infections, ensuring healthier and more productive flocks.



